Efficacy & Safety
The efficacy and safety of OXERVATE® were established in the largest clinical trial program conducted in patients with neurotrophic keratitis (NK)1
Efficacy
Complete and long-lasting resolution for most patients*1-4
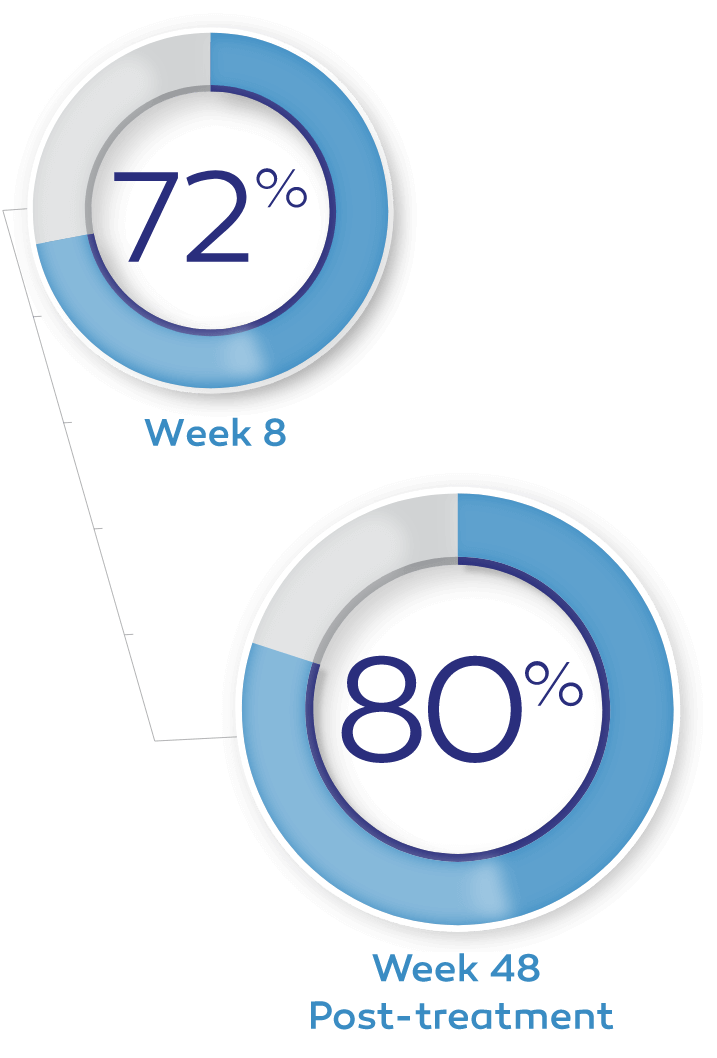
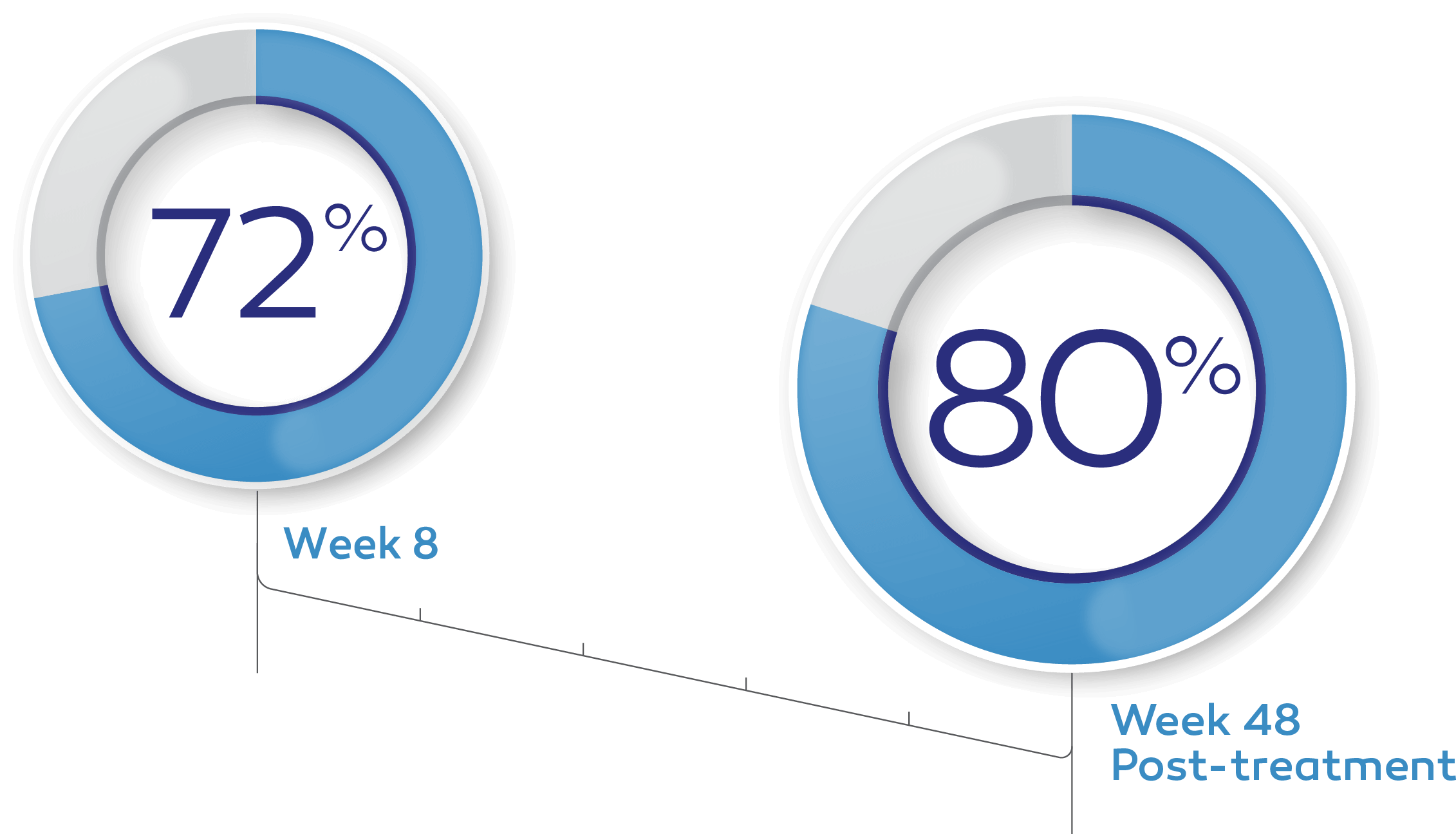
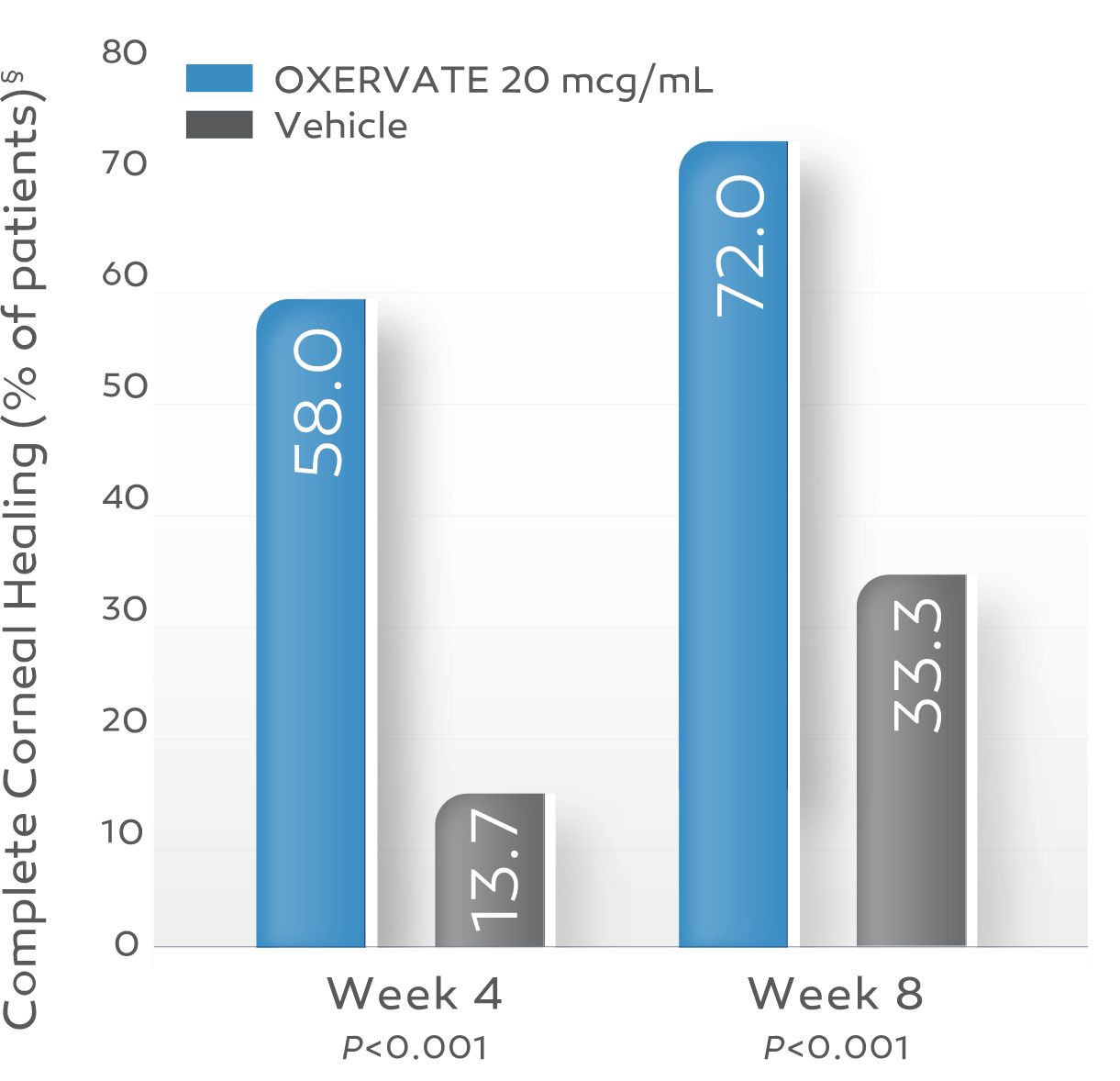
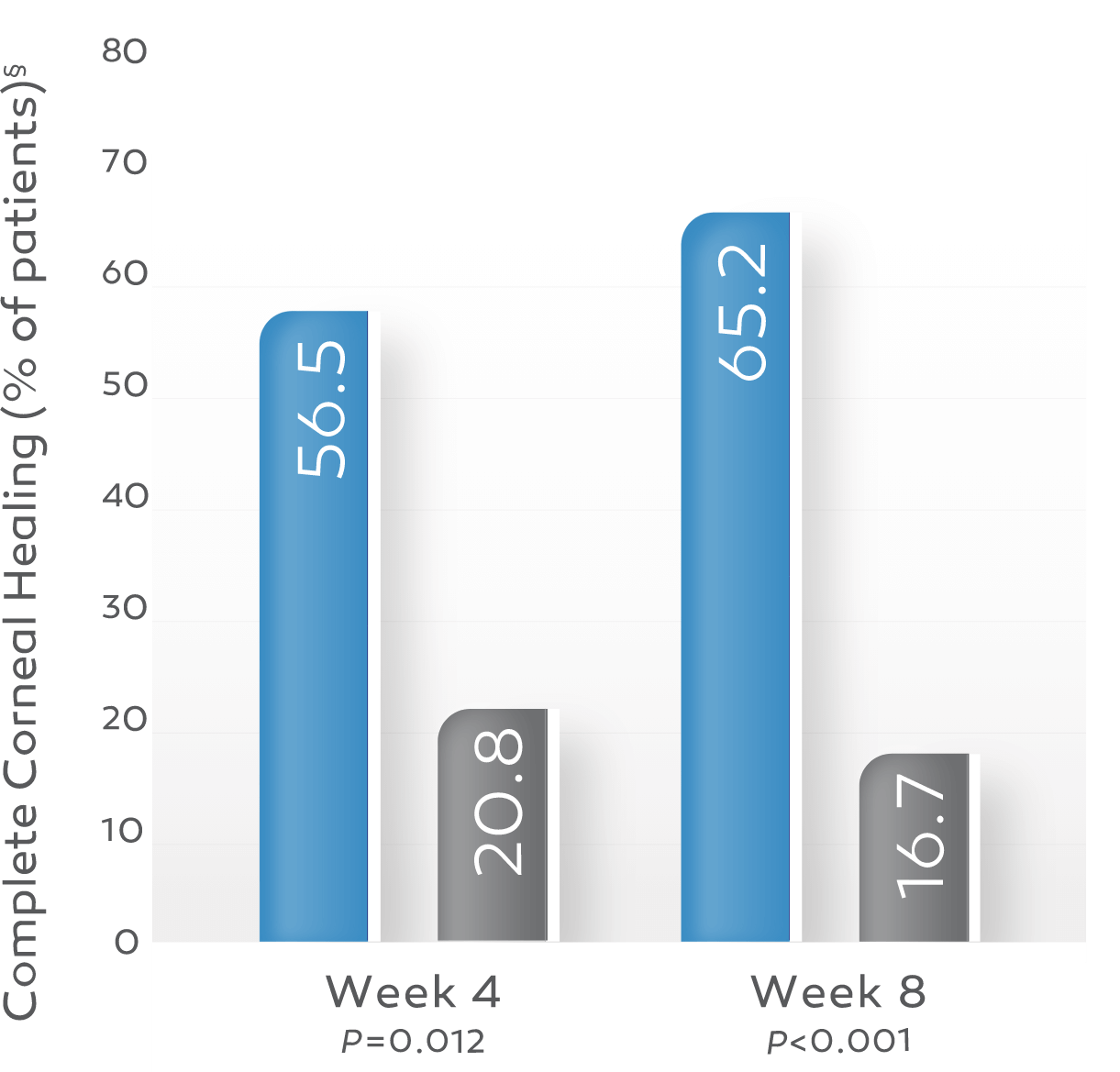
In clinical trials, up to 72% of patients achieved complete corneal healing at week 8 with a single course of therapy.*†1-3
Of the patients in the REPARO (Study NGF0212) trial who achieved complete corneal healing, 80% remained completely healed at 1 year.*4
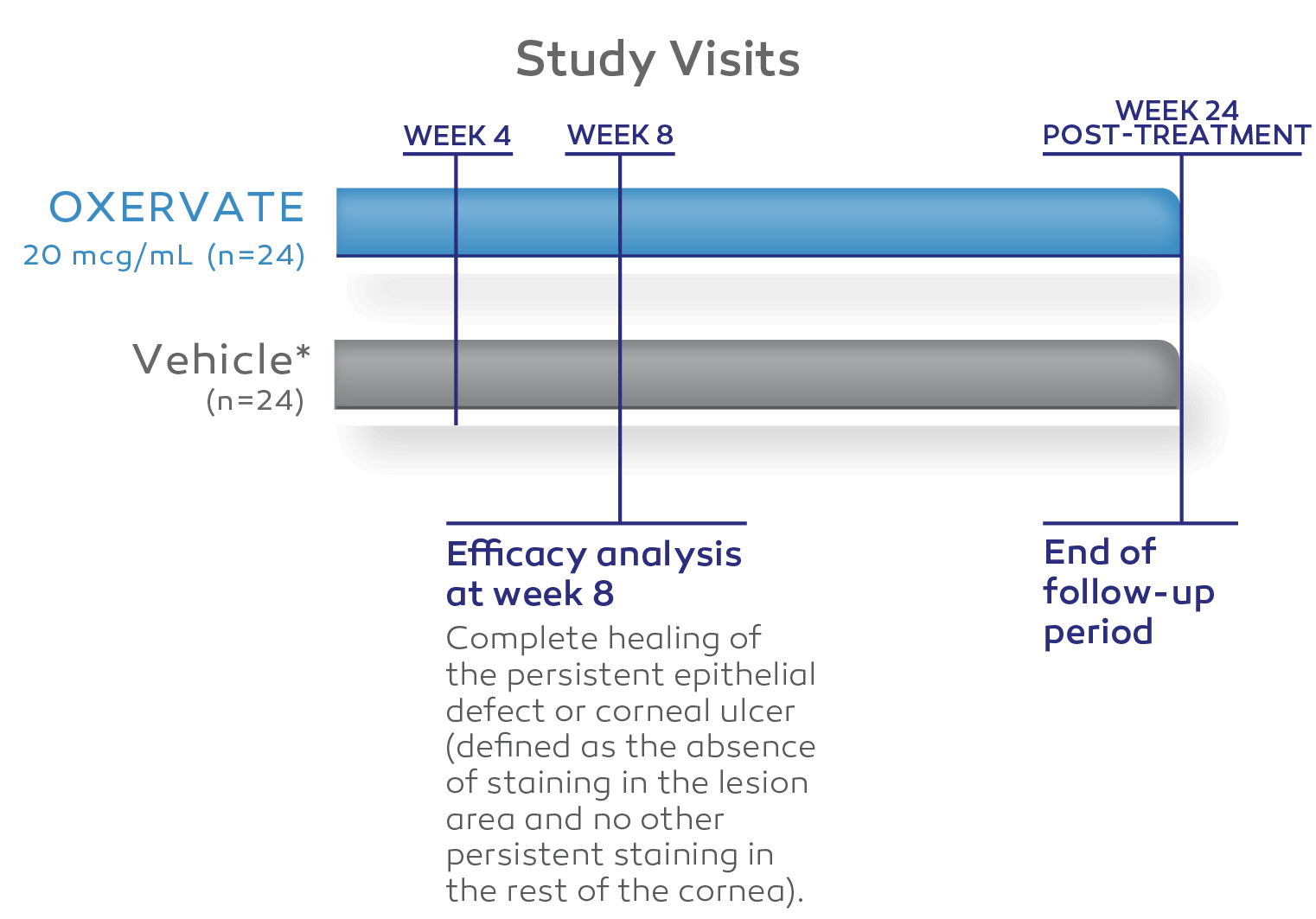
Resolution was evaluated in clinical trials as complete corneal healing, defined as the absence of staining in the lesion area and no persistent staining in the rest of the cornea after 8 weeks of treatment and as <0.5-mm lesion staining at 48-week follow-up.1-3
Key study findings were after 8 weeks of treatment, 6 times daily. REPARO (Study NGF0212): 52 patients with Stage 2 or 3 neurotrophic keratitis (NK) in 1 eye per group; 72% (36/50) of patients completely healed; vehicle response rate 33.3% (17/51). Study NGF0214: 24 patients with Stage 2 or 3 NK in 1 or both eyes per group; 65.2% (15/23) completely healed; vehicle response rate 16.7% (4/24). Last post-baseline observation carried forward; chi-squared test. Patients without any post-baseline measurements were excluded from the analysis.1-3
Up to 72% of OXERVATE®-treated patients achieved complete corneal healing*1-3
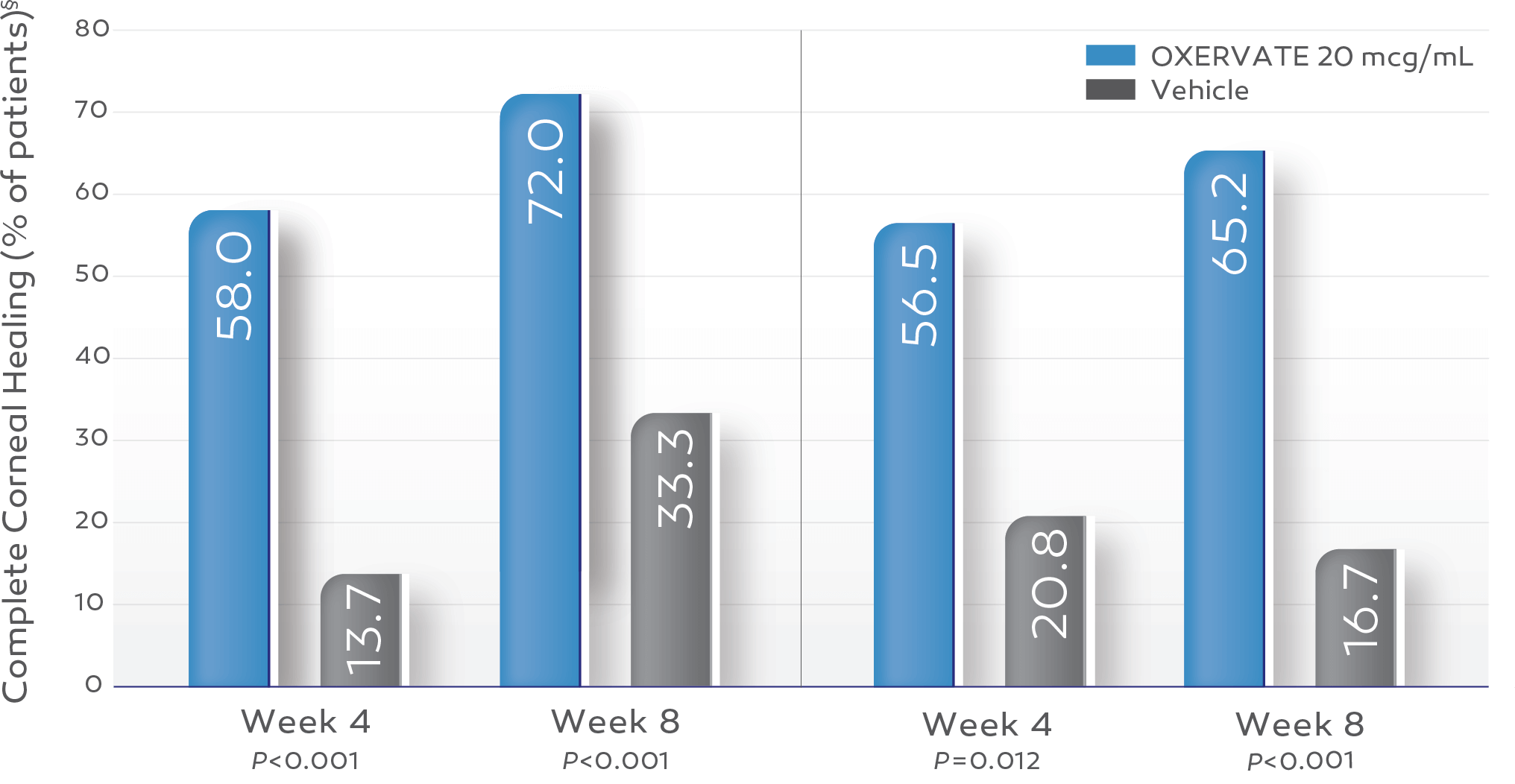
REPARO (Study NGF0212)†2
OXERVATE‡ 20 mcg/mL (n=50)
Vehicle (n=51)
Study NGF02143
OXERVATE 20 mcg/mL (n=23)
Vehicle (n=24)
§ Last post-baseline observation carried forward; chi-squared test. Patients without any post-baseline measurements were excluded from the analysis.
REPARO (Study NGF0212)†2
OXERVATE‡ 20 mcg/mL (n=50)
Vehicle (n=51)
Study NGF02143
OXERVATE 20 mcg/mL (n=23)
Vehicle (n=24)
§ Last post-baseline observation carried forward; chi-squared test. Patients without any post-baseline measurements were excluded from the analysis.
Complete corneal healing was defined as the absence of staining in the lesion area and no persistent staining in the rest of the cornea after 8 weeks of treatment.1-3
In REPARO, complete corneal healing (defined as <0.5-mm lesion staining) at 8 weeks was evaluated as a prespecified secondary endpoint. Additionally, as a post hoc efficacy analysis, corneal healing was reassessed more conservatively by masked central readers and was defined as 0-mm lesion staining and no other persistent staining outside of the lesion.2
The formulation that was tested in REPARO did not include the antioxidant methionine and is not the final formulation that is marketed as OXERVATE®. Methionine is an excipient added to the commercial formulation to improve its stability. More than 1 study was conducted with the final commercial formulation. No difference in safety was seen in either of the trials.
Study Design
Two independent, 8‑week, randomized, multicenter, double‑masked, vehicle‑controlled clinical trials1-3
REPARO (STUDY NGF0212) (EUROPE, N=156)*2

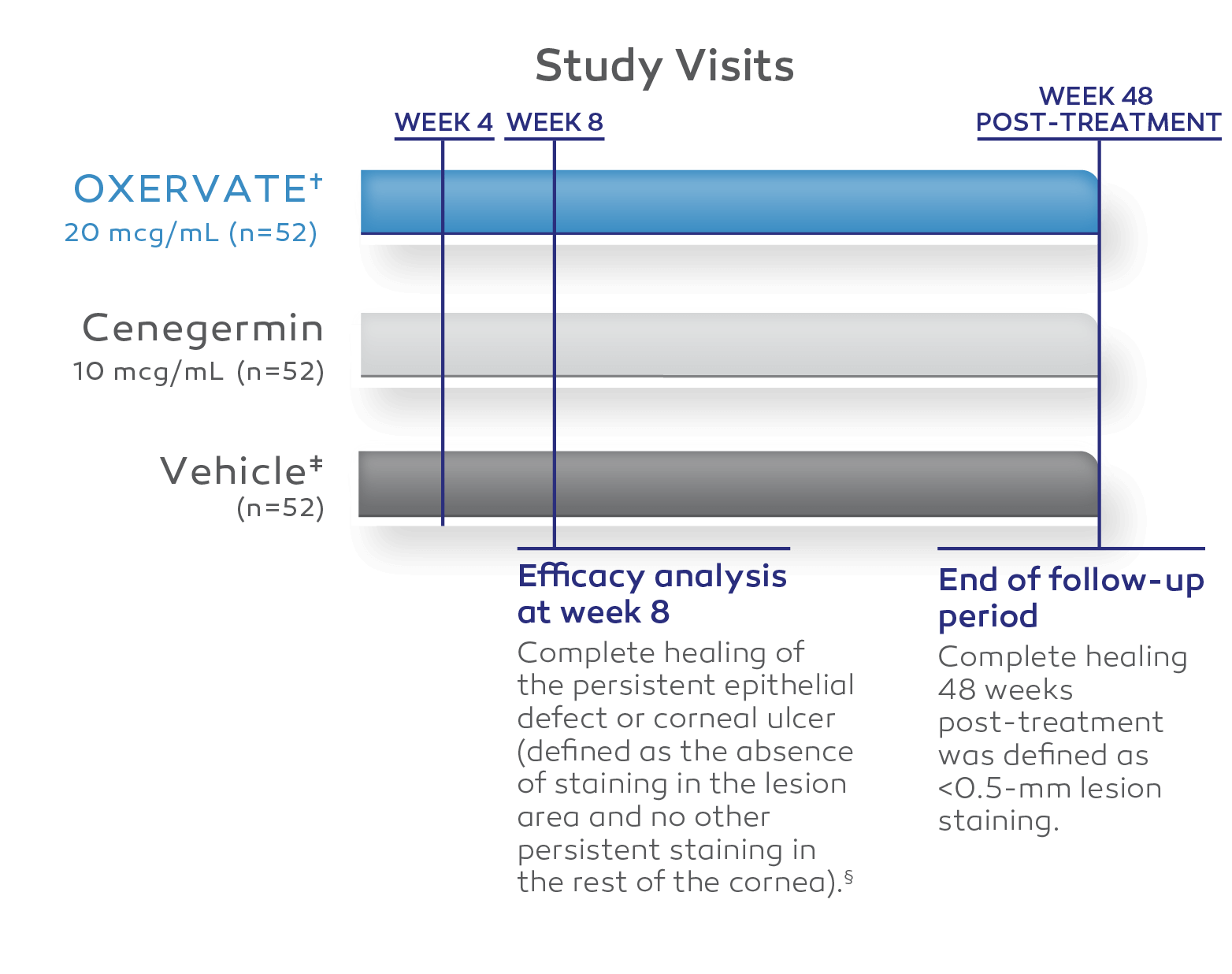
All patients enrolled had Stage 2 or Stage 3 neurotrophic keratitis (NK).2
Phase II study data only.
The formulation that was tested in REPARO did not include the antioxidant methionine and is not the final formulation that is marketed as OXERVATE. Methionine is an excipient added to the commercial formulation to improve its stability. More than 1 study was conducted with the final commercial formulation. No difference in safety was seen in either of the trials.
Twenty-three vehicle-treated patients were allowed to cross over, at their physicians’ discretion, to receive 8 weeks of uncontrolled treatment of cenegermin-bkbj 10 mcg/mL or cenegermin-bkbj 20 mcg/mL.2
In REPARO, complete corneal healing (defined as <0.5-mm lesion staining) at 8 weeks was evaluated as a prespecified secondary endpoint. Additionally, as a post hoc efficacy analysis, corneal healing was reassessed more conservatively by masked central readers and was defined as 0-mm lesion staining and no other persistent staining outside of the lesion.2
A diverse pool of patients with NK*
| OXERVATE 20 mcg/mL† (n=52) |
Vehicle (n=52) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Primary neurotrophic keratitis diagnosis, no. (%) Stage 2‡ Stage 3‡ |
27 (51.9) 25 (48.1) |
28 (53.8) 24 (46.2) |
| Underlying cause, no. (%) | ||
| Herpetic eye disease | 11 (21.2) | 18 (34.6) |
| Neurosurgical procedure | 8 (15.3) | 7 (13.4) |
| Other | 8 (15.3) | 5 (9.6) |
| Dry eye disease (DED) | 6 (11.5) | 5 (9.6) |
| Ocular surgery or procedure | 5 (9.6) | 7 (13.4) |
| Ocular surface injury/inflammation | 5 (9.6) | 5 (9.6) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 (7.7) | 4 (7.7) |
| Stroke | 2 (3.8) | 0 |
| Topical medication (glaucoma) | 1 (1.9) | 1 (1.9) |
| Unknown/unspecified | 1 (1.9) | 0 |
| Multifactorial | 1 (1.9) | 0 |
Baseline characteristics were similar across all treatment arms.2
The formulation that was tested in REPARO did not include the antioxidant methionine and is not the final formulation that is marketed as OXERVATE. Methionine is an excipient added to the commercial formulation to improve its stability. More than 1 study was conducted with the final commercial formulation. No difference in safety was seen in either of the trials.
Based on the Mackie classification.5
STUDY NGF0214 (UNITED STATES, N=48)3
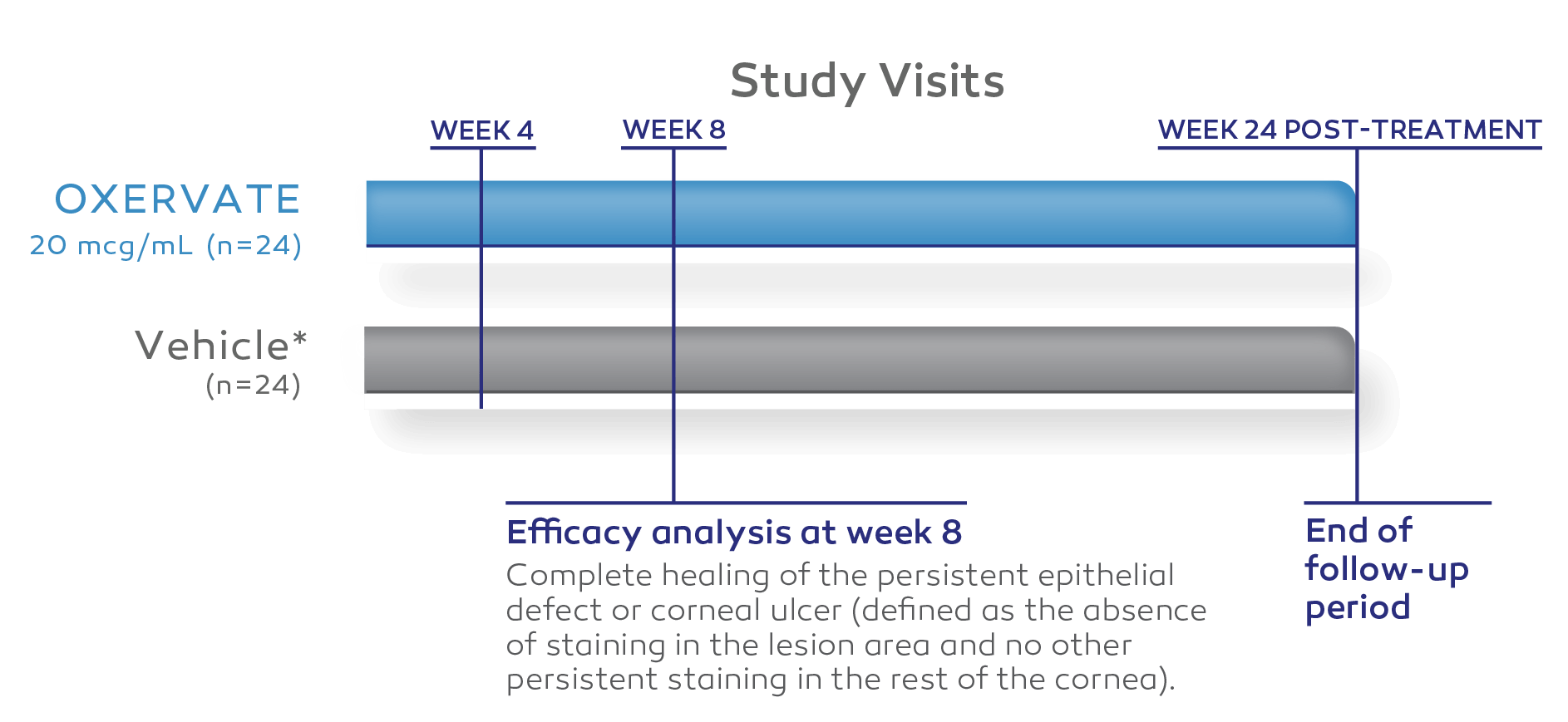
All patients enrolled had Stage 2 or Stage 3 NK.3
Thirteen vehicle-treated patients were allowed to cross over at their physicians’ discretion to receive 8 weeks of cenegermin-bkbj 20 mcg/mL.3
A diverse pool of patients with NK*
| OXERVATE 20 mcg/mL (n=24) |
Vehicle (n=24) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Primary neurotrophic keratitis diagnosis, no. (%) Stage 2† Stage 3† |
15 (62.5) 9 (37.5) |
18 (75.0) 6 (25.0) |
| Underlying cause, no. (%) | ||
| Herpetic eye disease | 9 (37.5) | 8 (33.3) |
| Ocular surgery or procedure | 3 (12.5) | 4 (16.7) |
| Other | 3 (12.5) | 4 (16.7) |
| Dry eye disease (DED) | 3 (12.5) | 3 (12.5) |
| Ocular surface injury/inflammation | 2 (8.3) | 1 (4.2) |
| Multifactorial | 2 (8.3) | 0 |
| Neurosurgical procedure | 1 (4.2) | 1 (4.2) |
| Topical medication (glaucoma) | 1 (4.2) | 0 |
| Unknown/unspecified | 0 | 2 (8.3) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0 | 1 (4.2) |
| Stroke | 0 | 0 |
Baseline characteristics were similar across all treatment arms.3
Based on the Mackie classification.5
Clinical Outcomes
Most patients experienced complete healing of the corneal surface*1-3
Images show a neurotrophic corneal lesion from baseline to week 8 in an actual patient treated with OXERVATE® in the REPARO (Study NGF0212) trial. Results are not indicative of all patients.
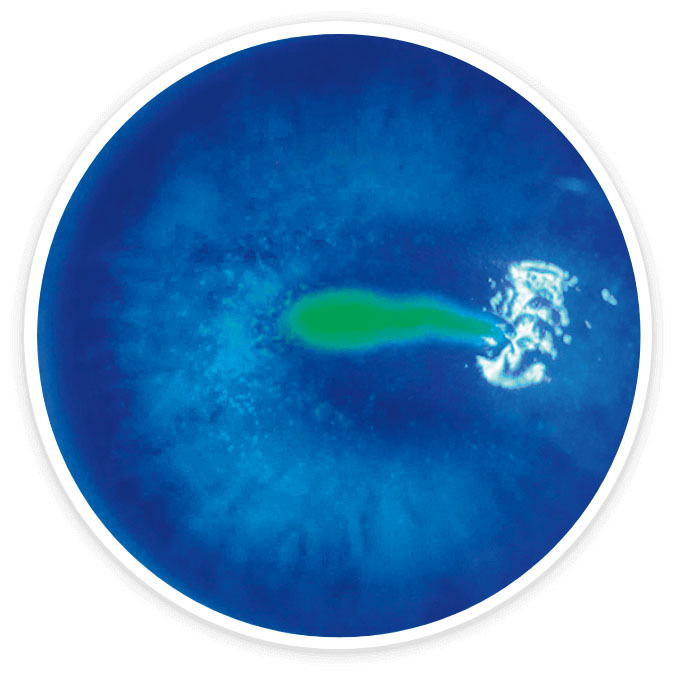
Baseline
Stage 2 NK
History of herpes zoster and diabetes
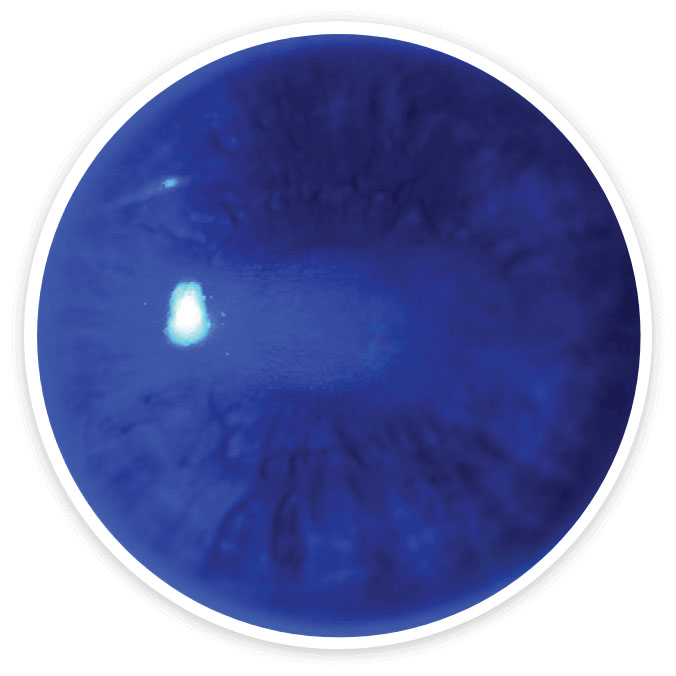

Week 8
Complete corneal healing*
Complete corneal healing was defined as the absence of staining of the lesion area and no persistent staining in the rest of the cornea after 8 weeks of treatment.1-3
Get information on real-world patients treated with OXERVATE
Safety Profile
OXERVATE® was generally well tolerated in clinical trials2,3
Contact lenses should be removed before applying OXERVATE1
- The presence of a contact lens (either therapeutic or corrective) could theoretically limit the distribution of cenegermin-bkbj onto the area of the corneal lesion
- Lenses may be reinserted 15 minutes after administration
OXERVATE may cause mild to moderate eye
discomfort such as eye pain during treatment1
- Advise patients to contact their doctor if a more serious eye reaction occurs
- In clinical trials, the most common adverse reaction was eye pain following instillation, which was reported in approximately 16% of patients. Eye pain may arise as corneal healing occurs
- Other adverse reactions occurring in 1% to 10% of OXERVATE patients included corneal deposits, foreign body sensation, ocular hyperemia, ocular inflammation, photophobia, tearing, and headache