
Efficacy & Safety
The efficacy and safety of OXERVATE® were established in the largest combined clinical trial program conducted in patients with neurotrophic keratitis (NK).1,2
Study Design
Two 8‑week, randomized, multi-center, double‑masked, vehicle‑controlled clinical trials3
All patients enrolled had Stage 2 or Stage 3 neurotrophic keratitis (NK).1
Phase 2 data only, Study NGF0212 (REPARO) was a phase 1/2 study.1
The formulation that was tested in Study NGFO212 (REPARO) did not include the antioxidant methionine and is not the final formulation that is marketed as OXERVATE. Methionine is an excipient added to the commercial formulation to improve its stability. More than 1 study was conducted with the final commercial formulation. No difference in safety was seen in either of the trials.4
Study NGF0212 (REPARO)1
| OXERVATE 20 mcg/mL† (n=52) |
Vehicle (n=52) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Primary neurotrophic keratitis diagnosis, no. (%) Stage 2 Stage 3 |
27 (51.9) 25 (48.1) |
28 (53.8) 24 (46.2) |
| Investigator-determined etiology,* no. (%) | ||
| Herpetic eye disease | 11 (21.2) | 18 (34.6) |
| Neurosurgical procedure (eg, acoustic neuroma, unspecified) | 8 (15.4) | 7 (13.5) |
| Other (eg, polyneuropathy, traumatic erosion, multifactorial) | 7 (13.5) | 3 (5.8) |
| Dry eye disease | 6 (11.5) | 5 (9.6) |
| Ocular surgery or procedure (eg, cataract surgery/scleral buckle/vitrectomy) | 5 (9.6) | 7 (13.5) |
| Ocular surface injury/inflammation (eg, chemical burn, unspecified) | 5 (9.6) | 5 (9.6) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 (7.7) | 4 (7.7) |
| Stroke | 2 (3.8) | 0 |
| Topical medication (glaucoma) | 1 (1.9) | 1 (1.9) |
| Unknown origin | 1 (1.9) | 0 |
Not an all-inclusive list of the investigator-determined etiologies of NK in NGF0212.
The formulation that was tested in Study NGF0212 (REPARO) did not include the antioxidant methionine and is not the final formulation that is marketed as OXERVATE. Methionine is an excipient added to the commercial formulation to improve its stability. More than 1 study was conducted with the final commercial formulation. No difference in safety was seen in either of the trials.4
All patients enrolled had Stage 2 or Stage 3 neurotrophic keratitis (NK).2
Study NGF02142
| OXERVATE 20 mcg/mL (n=24) |
Vehicle (n=24) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Primary neurotrophic keratitis diagnosis, no. (%) Stage 2 Stage 3 |
15 (62.5) 9 (37.5) |
18 (75.0) 6 (25.0) |
| Investigator-determined etiology,* no. (%) | ||
| Herpetic eye disease | 9 (37.5) | 8 (33.3) |
| Ocular surgery or procedure (eg, anterior and posterior surgeries, cataract surgery) | 3 (12.5) | 4 (16.7) |
| Dry eye disease | 3 (12.5) | 3 (12.5) |
| Other (eg, topical medication, unknown origin) | 2 (8.33) | 5 (20.8) |
| Ocular surface injury/inflammation (eg, chemical burn/multiple transplant surgeries) | 2 (8.3) | 1 (4.2) |
| Multifactorial | 2 (8.3) | 0 |
| Neurosurgical procedure (eg, trigeminal ablation, unspecified) | 1 (4.2) | 1 (4.2) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0 | 1 (4.2) |
Not an all-inclusive list of the investigator-determined etiologies of NK in NGF0214.
Study Results
OXERVATE clinical trial efficacy
The efficacy and safety of OXERVATE for the treatment of NK were studied in a total of 151 patients, evaluated in two 8-week, randomized, multi-center, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies3
Patients received study treatment dosed 6 times daily in the affected eye(s) for 8 weeks.3

In clinical trials complete corneal healing was defined as absence of staining of the corneal lesion and no persistent staining in the rest of the cornea at 8 weeks of treatment.3
Patients without any post-baseline measurements were excluded from the analysis.
In patients who were healed after 8 weeks of treatment with OXERVATE, recurrences occurred in ~20% of patients in Study NGF0212 and 14% of patients in Study NGF0214.3
Clinical Outcomes
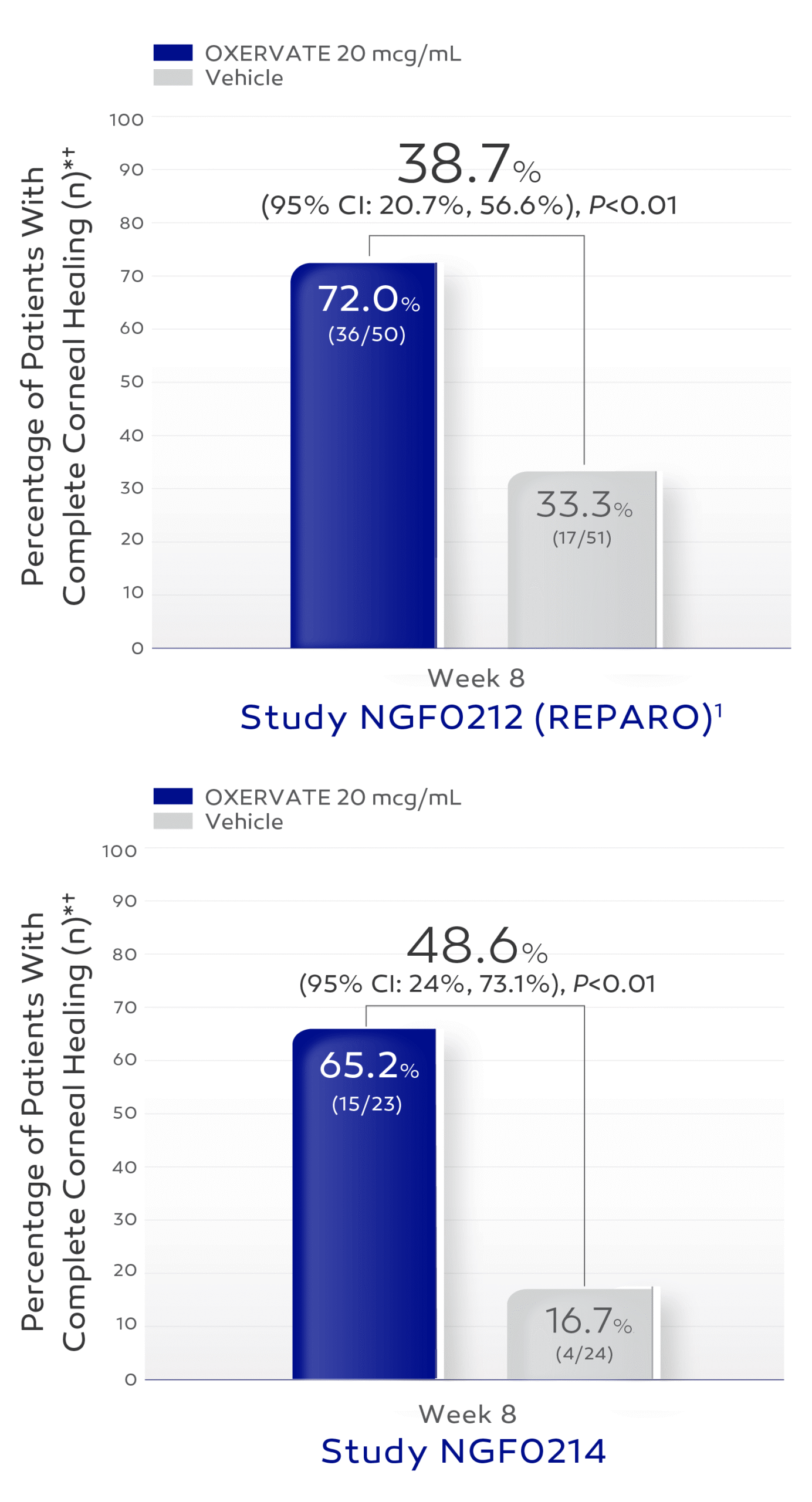
Many patients in the pivotal trials achieved complete corneal healing at week 8*3
Images are of a clinical trial patient with Stage 2 neurotrophic keratitis (NK) at baseline and week 8. Evaluations conducted by independent central reading center of the clinical images of corneal fluorescein staining. Not all patients in the trials achieved complete corneal healing.
Individual results may vary.5
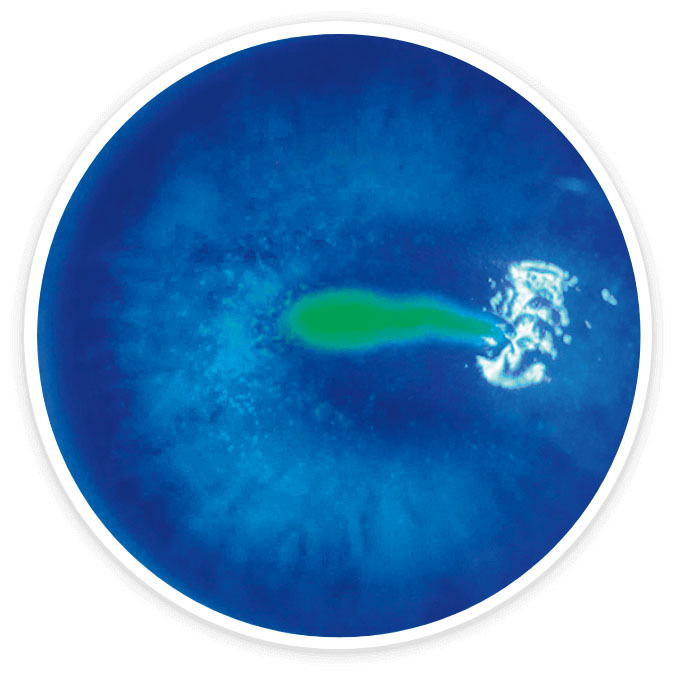
Baseline6
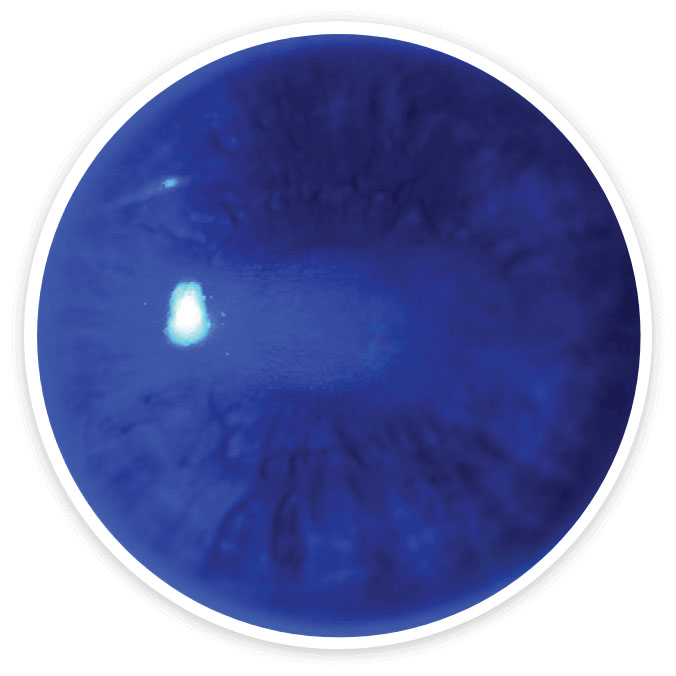

Week 86
Complete corneal healing6
The efficacy and safety of OXERVATE for the treatment of neurotrophic keratitis were studied in a total of 151 patients, evaluated in two 8-week, randomized, multi-center, double-masked, vehicle-controlled studies. In NGF0214, the percentage of patients with complete corneal healing at week 8 was 65.2% (15/23) in the OXERVATE arm vs 16.7% (4/24) in the vehicle arm with a treatment difference of 48.6% (95% CI: 24%, 73.1%; P<0.01). In NGF0212, the percentage of patients with complete corneal healing at week 8 was 72% (36/50) in the OXERVATE arm vs 33.3% (17/51) in the vehicle arm with a treatment difference of 38.7% (95% CI: 20.7%, 56.6%; P<0.01). Patients without any post-baseline measurements were excluded from the analysis.3
In clinical trials, complete corneal healing was defined as absence of staining of the corneal lesion and no persistent staining in the rest of the cornea at 8 weeks of treatment.3
Safety Profile
OXERVATE® safety in clinical trials3
- In clinical trials, the most common adverse reaction was eye pain following instillation, which was reported in approximately 16% of patients3
- Eye pain may arise as corneal healing occurs3
- Other adverse reactions occurring in 1% to 10% of OXERVATE patients included corneal deposits, foreign body sensation, ocular hyperemia, ocular inflammation, photophobia, tearing, and headache3
Contact lenses should be removed before applying OXERVATE3
- The presence of a contact lens (either therapeutic or corrective) could theoretically limit the distribution of OXERVATE onto the area of the corneal lesion3
- Lenses may be reinserted 15 minutes after administration3
OXERVATE may cause mild to moderate eye discomfort such as eye pain during treatment. Advise patients to contact their doctor if a more serious eye reaction occurs3

